Table of Contents
Introduction: The Electric Revolution Is Here in 2024
Electric cars have ceased being a trend and have become the future of driving, and the future has already arrived in 2024. As the fuel prices continue to soar, as emission regulations further tighten, and as green technology develops by leaps and bounds, increasing numbers of people are choosing to go green by using electric vehicles (EVs).
Car manufacturers worldwide have taken the option of pushing the envelope in 2017 more than ever before. Electric cars of the new generation are ready to show a jaw-dropping range of possibilities, advanced technologies, and sustainability, both in sleek cars and heavy SUVs, and even in super-luxury cruise-like models.
This article brings 7 futuristic electric vehicles in 2024 that are revolutionizing how people drive automobiles. Be it a tech enthusiast, an environmental activist, or a regular person who needs to test the latest and coolest new car, these models certainly deserve consideration.
Now, it is time to know what the smartest, fastest, most futuristic electric cars of the year are.
1. Tesla Model S Plaid: Still Leading the Pack
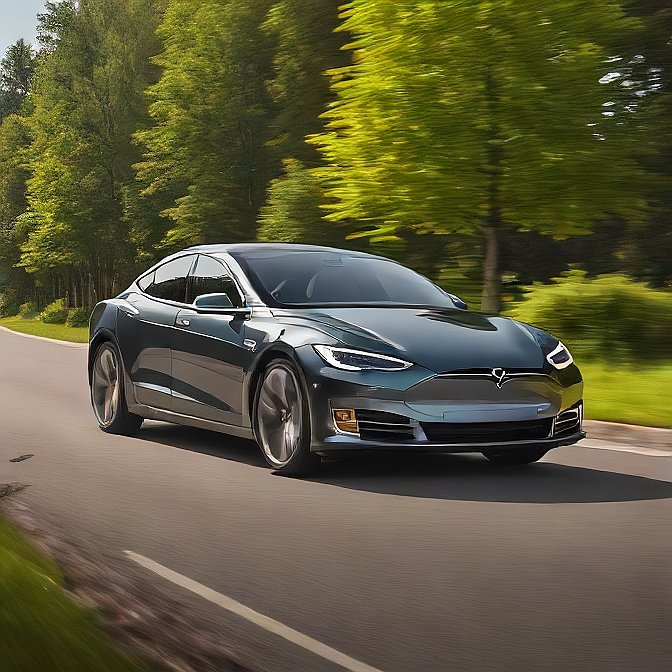

Tesla Model S Plaid will be in its lead in 2024 due to its unparalleled speed and advanced technology. It’s 0-60mph in the range of 2 seconds is also very nice, and it is one of the quickest electric cars in the world.
It not only has a long driving range but also, Tesla continues to update its software, so features such as Autopilot and Full Self-Driving will get smarter in the future. Elegant design and modern interior make the Model S Plaid one of the best picks for technology and performance drivers and fans.
2. Lucid Air Sapphire: Pure Luxury Meets Electric Speed
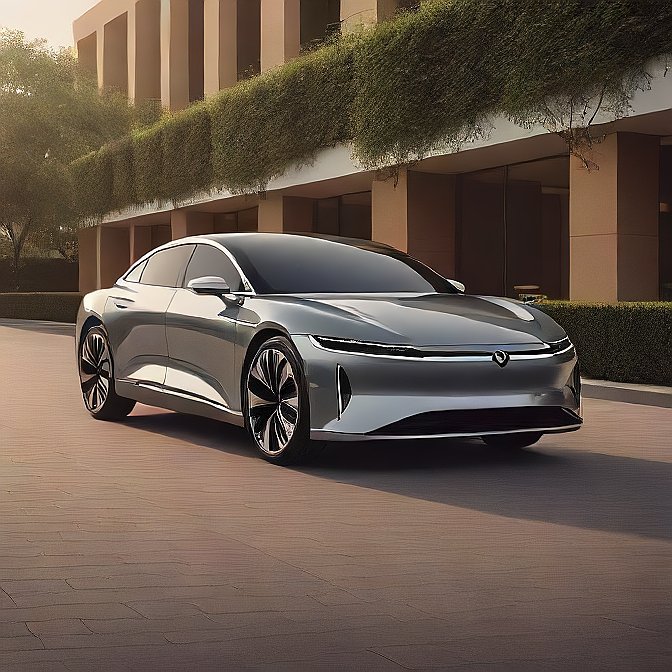

The Air Sapphire, 2024, is a new, increasing bar set by Lucid Motors. This hyper-luxury EV is a jaw-dropping acceleration mixed with very high-end craftsmanship. It is specified for people who desire comfort and speed.
The Sapphire offers a beautiful design inside, a large cabin, and one of the most powerful charge levels ever known. Given that it is a formidable rival to Tesla’s hegemony, the high-touch quality and superior driver technology is what endear the Lucid Air Sapphire to close attention.
3. Rivian R1S: The Rugged Electric SUV for All Terrains
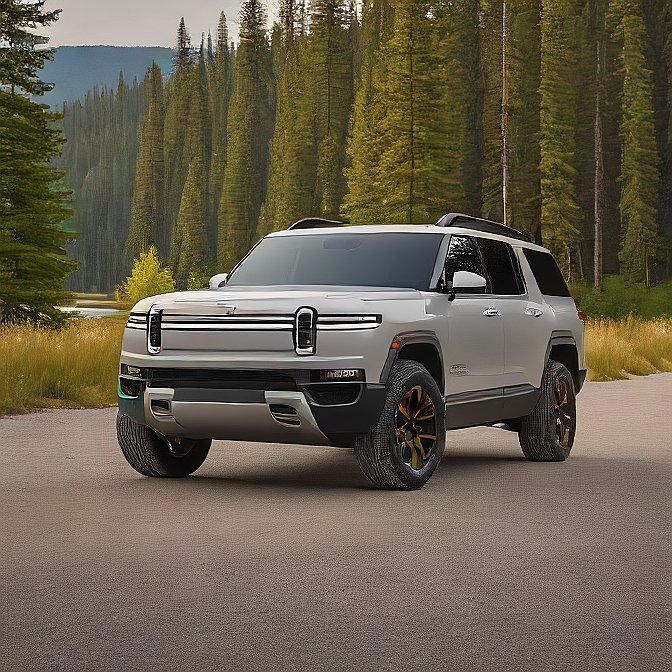

Is a no-nonsense, fast and efficient electrically powered, large SUV, designed to navigate city streets as well as unpaved trails, what you need? The Rivian R1s is designed to go where you need to go. It is an adventure vehicle with proper features in this all-electric SUV, as this one has flexible air suspension, a quad-motor-based drive, and a range of up to 400 miles.
It has a pragmatic and high-tech cabin, over-the-air updates, and is heavily committed to being eco-friendly. By 2024, Rivian will have built a network of delivery centers so that the R1s can be accessed by families as well as off-road enthusiasts.
4. Mercedes-Benz EQS: Electric Intelligence in Motion
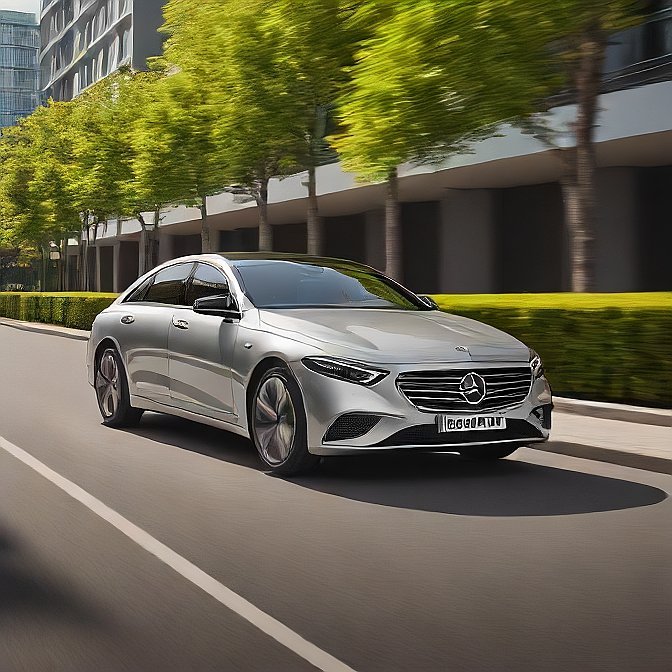

Mercedes-Benz EQS is a German luxury car with an innovative electric touch of the future. This 2024 model is still remarkable with its silent and smooth drive and the interior as a five-star lounge.
The intuitive MBUX Hyperscreen, enhanced driver-assist systems, and best safety ratings are what make it stand out. Another big company that is up to the challenge in developing the future of electric cars is Mercedes, which will be adding several EQ models and focusing on the European market.
Check Out: Apple vs Samsung in 2025: Which Tech Giant Is Winning?
5. Ford F-150 Lightning: Power and Performance for the People
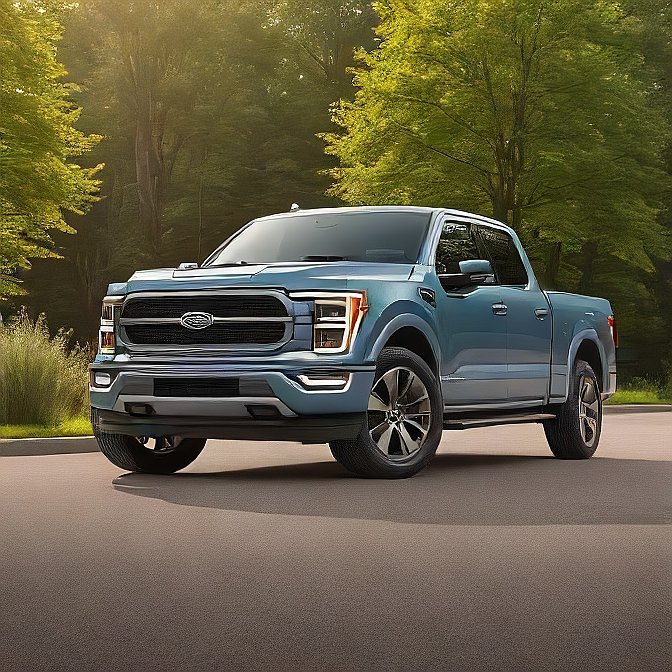

The legendary pickup truck of the brand Ford has become electric, and the 2024 F-150 Lightning shows that electric vehicles can be both efficient and strong. It can work and play with high towing capacities and numerous power outlets, plus an onboard generator.
The Lighting has power back-up to the vehicle and smart connectivity features via a mobile service provided by Ford, and it is most interesting that it still has multiple trim levels to ensure that it is affordable to the common man and make it one of the trusted purchases in the United States and for small business owners.
6. Hyundai Ioniq 6: Futuristic Design with Real-World Efficiency
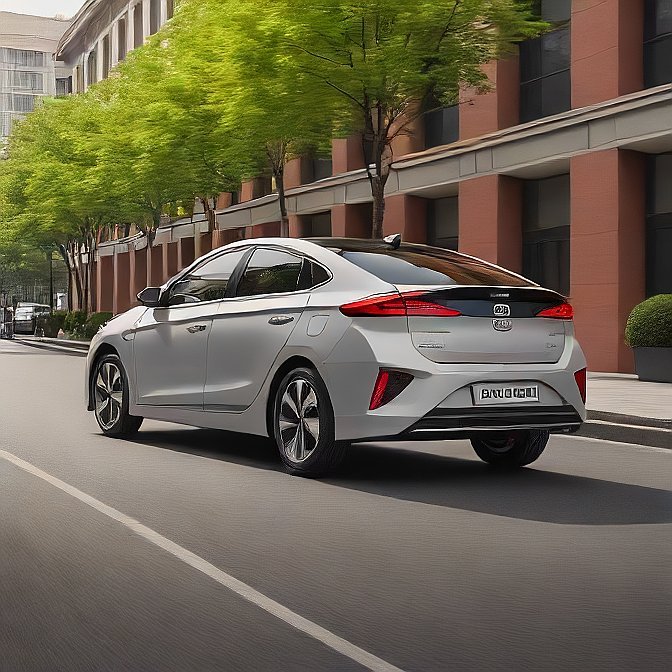

In 2024, the Hyundai Ioniq 6 will have a swanky body and a terrific range to boot. This is a midsize electric sedan that manages to integrate innovation and affordability, which makes it one of the outstanding cars in the mid-range electric car market.
It has the best infotainment technology, security features, and environmentally friendly materials. The Ioniq 6 does so whether on a commute or road trip, making it comfortable, affordable, and power-packed without any significant damage to the environment.
7. BMW i7: The Ultimate Electric Driving Machine
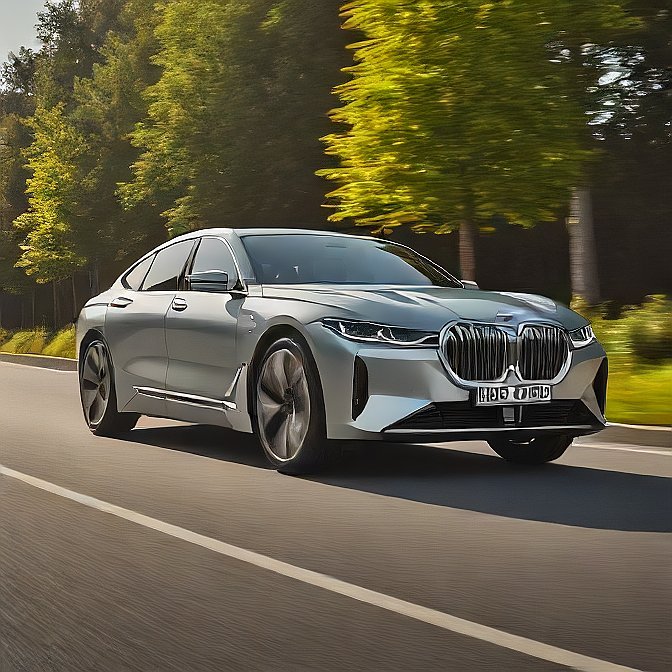

Sporting a powerful, fully electric powertrain, BMW is launching the i7- a luxury car that will compete in an EV luxury race. The 2024 i7 reflects the company’s commitment to sustainability because it uses recycled goods and green manufacturing.
On the inside, the i7 has one of the most immersive digital experiences in the market with its inclusion of a huge theater screen at the back of the vehicle. It is rapid, hushed, and also brimming with technology, which means it is a good rival in the high-performance electric car segment.
Bonus Section: What Makes a High-Tech Electric Car in 2024?
In 2024, electric cars are not merely battery-powered automobiles with the capacity to drive smartly and be connected to everything, but with the packaging of futuristic features. This is the real definition of a high-tech electric car this year:
- Fast Charging Capabilities
- The best EVs are now capable of fast DC charging, which gives you the possibility to get hundreds of driving miles in a little more than 20 to 30 minutes. That renders the electric cars much more viable as distance-friendly vehicles.
- AI-Powered Driving Systems
- Current EVs incorporate artificial intelligence in many aspects, whether it is intelligent cruise control or full self-driving. Tesla, Mercedes, and BMW are leading in the field of systems that will automatically learn your driving behaviors and make the road safer.
- Integration with Mobile Apps and EV Networks
- The electric cars with high technology have easy control via apps on your smartphone – allowing you to preheat your car or warm up the cabin, find the nearest chargers, program charging, and the current range in real-time.
- Range, Performance, and Over-the-Air Updates
- The latest electric vehicles are capable of longer distances (300+ miles), can accelerate, and can be powerful to handle. Better yet, most EVs can be updated automatically over the air to new versions which not only increase performance but also introduce new features without the need to even go to a service center.
Such features will make the electric cars in 2024 more intelligent, speedy, and connected than ever before, rewriting the expectations that we may have about a car.
Why Electric Cars Are Gaining More Ground in 2024
It is not a coincidence that electric cars will be popular in 2024: it will come as the consequence of international technological, policy, and demand changes. Here’s why EVs are becoming the new normal:
Global Push for Clean Energy
Nations across the globe are setting up deadlines for eliminating gas-powered cars. This has compelled car manufacturers to put a lot of money into producing electric cars, which have become more visible and appealing.
Government Incentives and Tax Benefits
In most jurisdictions, the users of electric cars are provided with tax credits or reduced car registration costs, or even free energy. The benefits suggest that EVs are cost-effective and encourage the customer to be environmentally friendly.
Advancements in Battery Technology
Battery efficiency has improved significantly. The new batteries have higher energy density, charge faster, and last longer, and several of the key gripes of the first electric cars are being addressed with contemporary batteries.
Improved Charging Infrastructure
Investment by the public and private sectors in EV charging stations is increasing at a rapid pace. Nowadays, it is possible to find trustworthy chargers in cities, on highways, and even in rural districts, and the ownership of an electric vehicle becomes extremely easy.
As the world is leaning towards greener transportation, electric vehicles are leading the efforts towards a greener way of modern mobility, offering smart solutions to personal mobility.
Conclusion:
By 2024, eco-friendly electric cars will represent more than a solution with a low level of environmental impact; they are now the optimum performance, the ultimate in luxury or design features, making them highly advanced and long-range. Whether you want zippier performance than Tesla and sharper off-roading than Rivian or just online luxury with BMW, there is an electric car to suit every type of driver.
The thing about this year is that the car manufacturers are not just concentrating on innovation, but more on accessibility. It does not matter whether you are looking to get your initial EV or intend to make an upgrade; the 2024 lineup offers you numerous high-tech, sustainable, and easy-to-use models to consider.
With the current state of charging networks becoming better than ever and technology more advanced than ever, there has never been a better time to join the electric movement.
For more info: Click Here.
FAQs
Q1: What are the top electric cars in 2024?
There are Tesla Model S Plaid, Lucid Air Sapphire, Rivian R1S, Mercedes EQS, Ford F-150 Lightning, Hyundai Ioniq 6, and the BMW i7, the best year 2024 electric models. These are the most excellent in performance, technology, and range.
Q2: Are electric cars better than gas cars?
Yes, electric vehicles will cost less to drive, they will produce no exhaust gas, and they will drive smoothly. They also require less maintenance, and there is a tax benefit on them in most countries.
Q3: How far can electric cars go on a single charge in 2024?
Most of the new electric vehicles of 2024 will cover 250 to 400+ miles. The distance that other luxury EVs like the Lucid Air can cover is even greater.